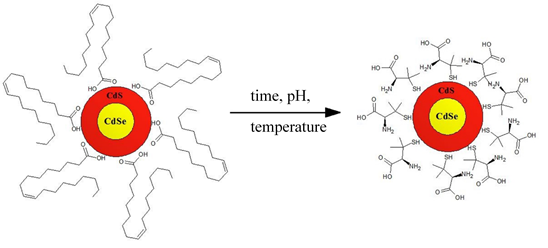
The surface chemistry plays an important role in quantum dots (QDs) properties, including their dispersibility, reactivity, stability, melting point or electron structure. Ligands at the QDs surface are key parameter in various QDs applications.
In our laboratory, we are using mainly ligand exchange methods to modify QDs surface properties and to add new functionalities to our nanostructures. This method allows attaching new chemicals to nanostructures surface keeping their hydrodynamic size constant or even making it smaller. Since 2016, we perform functionalization of various sizes and shapes of Cd- and Pb-based nanostructures by means of thiol-derived ligands, i.e. 3-mercaptopropionic acid (3-MPA), d- and l-penicillamine (LPA,DPA) or cysteamine (CA) – by optimizing the exchange of ligands in terms of various environmental streams, among others the effect of pH.